What are autoimmune diseases? What are the Causes? Treatment
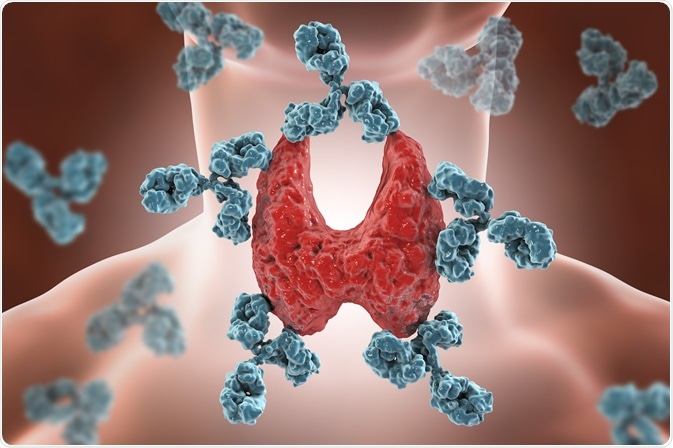
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system produces antibodies that attack the body’s own cells. There are many varieties, including celiac disease, lupus, and Graves’ disease. Although they cannot be cured, there are several treatment options available to manage symptoms and reduce further damage to your body.
There are about 80 different autoimmune disorders, ranging in severity from mild to disability, depending on which system of the body is under attack and to what degree. For unknown reasons, women are more susceptible than men, especially during the childbearing years. It is thought that sex hormones may be at least partially responsible. There is usually no cure, but the symptoms of autoimmune disorders can be managed.
What is the immune system?
The immune system includes different parts of the body, including the sensible blood cells, skin, bone marrow, and more that work to keep you healthy. The immune system protects you from infection by detecting and fighting diseases.
If infectious diseases such as bacteria or viruses enter your body, immune cells often kill or crush them, eliminating the infection. This is known as an immune reaction.
Autoimmune disease occurs when the immune system attacks healthy organs and tissues instead of attacking bacteria, viruses, or other sources of infection.
immune system malfunction
Immune system cells called T lymphocytes (T cells) use special receptors on their surface to identify foreign microbes such as bacteria and viruses. T cells, which often react to the body’s tissues, are destroyed by the thymus, an organ of the immune system located behind the breastbone. ‘Self-attacking’ T cells escaping destruction can be activated by a trigger. The exact triggers are unknown, but viral infections and hormones are amongst the suspects. The rogue T cells then instruct the B lymphocytes (B cells) to make antibodies against a certain tissue, organ, or system. These types of antibodies are called “autoantibodies”.
What are the causes of autoimmune disease?
Although more than one person with an autoimmune disease has a genetic predisposition, it is not known why autoimmune diseases develop. An environmental factor such as infection, voltage, medication, diet, and even ultraviolet radiation then triggers the symptoms of autoimmune disease.
Types of autoimmune diseases and their symptoms
There are more than 100 different autoimmune diseases. Many of these are long-term illnesses, with symptoms varying in severity over time. Some of the more common autoimmune diseases include:
- celiac disease – the immune system reacts to gluten (found in wheat and other grains) and damages the small intestine. Celiac disease causes gas, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
- Lupus– many parts of the body can be affected, including the skin, muscles, joints, lungs, heart and kidneys.
- rheumatoid arthritis– bone and cartilage are damaged, causing tender, swollen and stiff joints.
- Graves’ disease– the thyroid gland is very active, causing anxiety, heart palpitations, weight loss and irritation or puffy eyes.
- multiple sclerosis– the border system is affected, causing muscle weakness and poor alignment, vision problems, and in some cases, cognitive difficulties.
- type 1 diabetes – the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to manage blood sugar levels. The first symptoms may include thirst, hunger, and frequent urination.
Many people have signs and symptoms of autoimmune disorders for a long time before seeking help. Diagnosing an autoimmune disease can also take a long time, as some symptoms such as fatigue and ‘feeling unfit’ are common to many adults, while symptoms can come and go. In many conditions, there is no single test that confirms the diagnosis.
See your doctor if you think you may have an autoimmune disease. They will examine your symptoms more closely, examine you, and ask about your general well-being. They may order a blood test, X-ray, MRI or biopsy… Depending on your situation, your physician may also refer you to a specialist for further research or advice on treatment options.
Treatment of autoimmune disease
While there is no cure for autoimmune diseases, there are several treatments available to manage symptoms and reduce further damage to your body. Individuals diagnosed with autoimmune diseases often benefit from:
- a healthy
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Getting the right combination of lots of sleep, rest and training
- Reducing tension if possible and finding ways to deal with inevitable tension
Certain medications and lifestyle modifications can help autoimmune diseases. For example, people with type 1 diabetes inject insulin, while those with autoimmune diseases that affect the skin are advised about sun exposure, bathing, creams and lotions. Individuals with celiac disease should follow a gluten-free diet.
While some people may have mild autoimmune diseases, others will need to devote a lot of time and care to managing their condition. However, more than one person with autoimmune conditions can live full and enjoyable lives.
- On-Site Comments















Comment