What is myoma? 10 Symptoms and Treatment of Uterine Fibroids

Fibroids (uterine fibroids) are a common type of noncancerous tumor that can grow in and above your uterus. Not all fibroids cause symptoms, but fibroids symptoms can include heavy menstrual bleeding, back pain, frequent urination, and pain during sex. Small fibroids usually do not need treatment, but larger fibroids can be treated with medication or surgery.
Fibroids, or uterine fibroids, are growths or benign tumors that form inside the uterine wall. Seventy to 80 percent of women over the age of 50 will have fibroids. Only 20 to 30 percent will have fibroid symptoms. Fibroids It rarely enlarges in girls before puberty and in women after menopause. Pre-existing fibroids stop growing and may even shrink in women after menopause.
Fibroids are not usually an accidental issue, but they are sometimes associated with fibroids and infertility, miscarriage, and preterm birth. Other problems may include heavy, long and painful periods. Treatment depends on the size, number, and position of the fibroids, but may include medication, procedures under local anesthesia, ultrasound procedures, and surgery. Fibroids are rarely cancerous.If you wish, you can take a look at the Myomlu Ladies Club.
What is myoma (uterine fibroids)?
Uterine fibroids (also called leiomyomas) are growths of muscle and connective tissue from the wall of the uterus. These growths are usually non-cancerous (benign). An axilla in the private uterine pelvis is a pear-shaped organ. The usual size is the lemon-equivalent size of your uterus. It is also called the womb and is where a baby grows and develops during pregnancy.
 myoma
myomaFibroids can grow as a single nodule (single growth) or as a cluster. Fibroid clusters can range in size from 1 mm to more than 20 cm (8 inches) or larger. They can be as big as a watermelon for comparison. These growths can develop on the wall of the uterus, the main cavity of the organ, and even on its outer surface.
Fibroids can vary in size, number, and position within and above your uterus. uterine fibroids You may experience a variety of symptoms with fibroids, and they may not be exactly the same as another woman with fibroids. Because of how unique fibroids can be, your treatment plan will depend on your individual situation.
Who Is at Risk for Fibroids?
There are several risk factors that may play a role in your chances of developing fibroids. These may include:
- Obesity and higher body weight (a person is considered obese if they are more than 20% of their healthy body weight).
- Family history of fibroids.
- Not having children.
- Early onset of menstruation (having your period at a young age).
- Age late for menopause.
 uterine fibroids tumors
uterine fibroids tumorsWhere Do Fibroids Grow?
There are several places, both inside and outside of your uterus, where fibroids can grow. The location and size of your fibroids are valuable for your treatment. It will determine where your fibroids grow, how large they are and how many you have, which type of treatment will work best for you, or even whether treatment is necessary.
What Are the Types of Fibroids?
There are different names given to the places where your fibroids are located in and on the uterus. These names describe not only where the fibroid is, but also how it is attached.
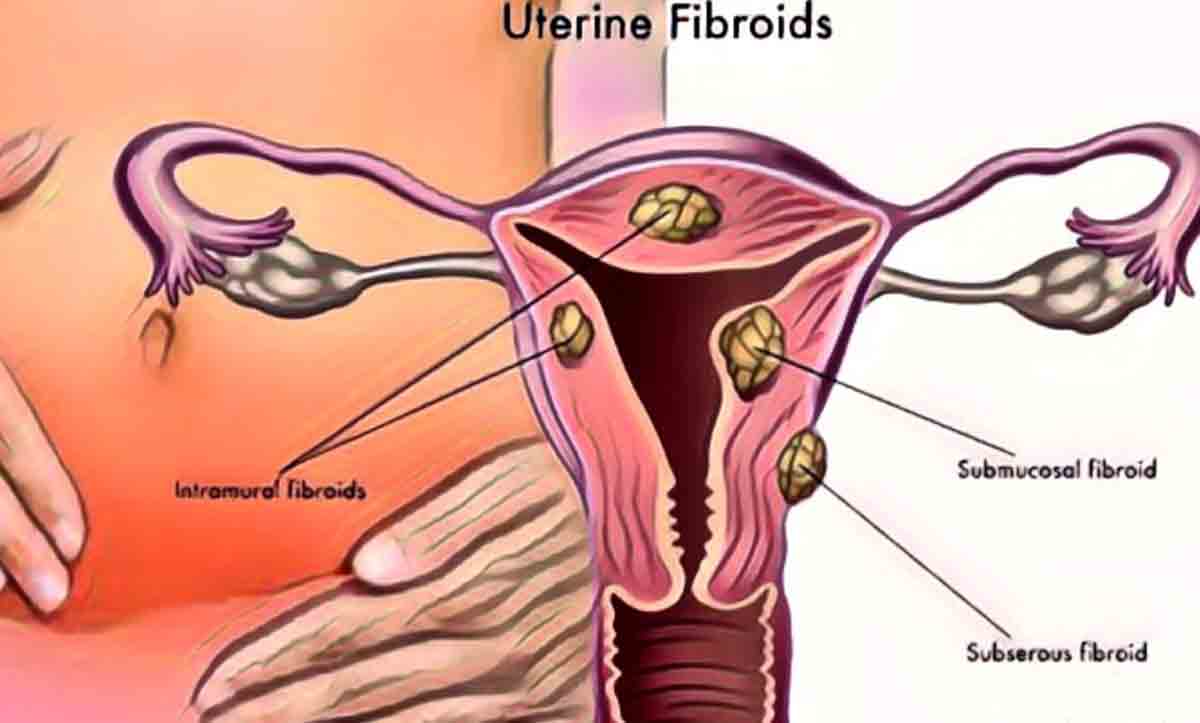 types of fibroids fibroids
types of fibroids fibroidsSpecific places where you can have uterine fibroids include:
Submucosal Fibroids
In this case, the fibroids grow within the uterine cavity (space) where the baby grows during pregnancy. Consider the growths extending into the empty space in the middle of the uterus.
Intramural Fibroids
These fibroids are embedded in the uterine wall. Imagine the sides of the uterus as the walls of a dwelling. Fibroids grow inside this muscle wall.
Subserous Fibroids
This time, these fibroids, located outside the uterus, are closely attached to the outer wall of the uterus.
Pedicle Fibroids
These fibroids, which are the least common type, are also found outside the uterus. But peduncle fibroids are attached to the uterus by a thin stalk. They are often described as mushroom-like because they have a stem and then a much wider apex.
Are fibroids cancer?
It is extremely rare for a fibroid to go through changes that turn it into a cancerous or malignant tumor. In fact, one in 350 women with fibroids will develop a malignant tumor (malignant).
 myoma cancer symptoms
myoma cancer symptomsThere is no 100% predictable test for detecting rare fibroid-associated cancers. However, individuals with rapid growth of uterine fibroids or fibroids that grow during menopause should be evaluated promptly.
What Are the Symptoms of Fibroids?
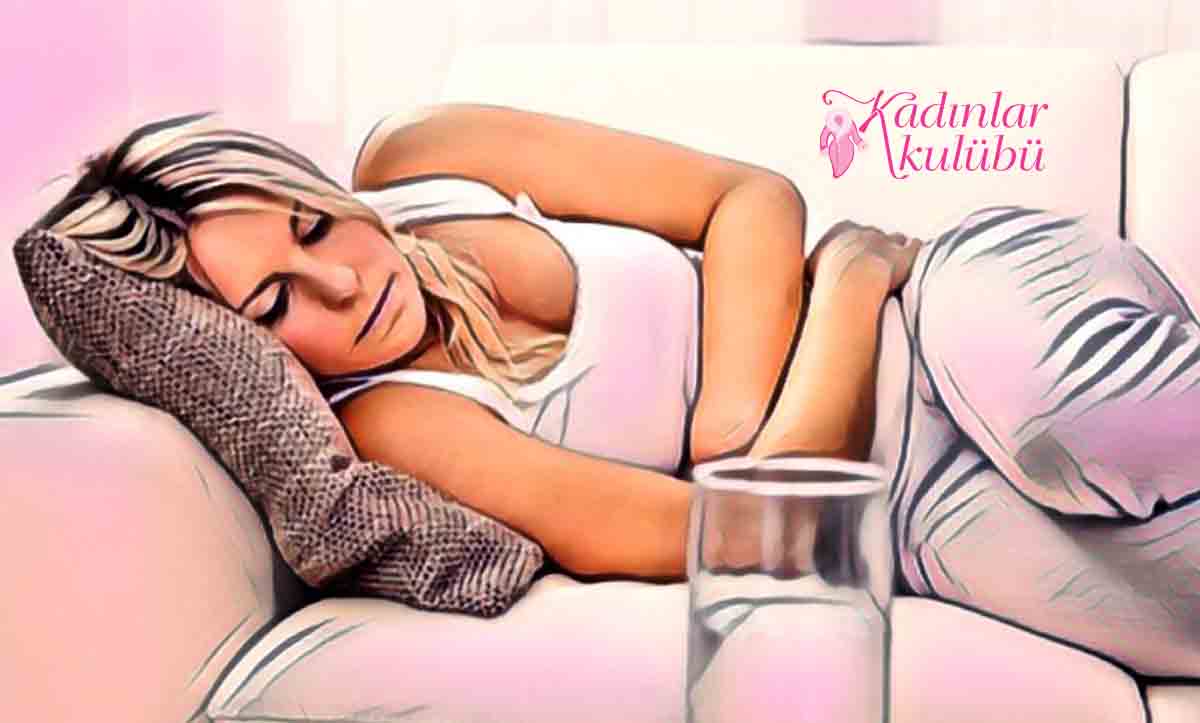
Most fibroids do not cause any symptoms and do not require treatment other than the regular observation of your healthcare professional. These are typically small fibroids. When you don’t experience symptoms, it’s called an asymptomatic fibroid.
 what are the symptoms of fibroids
what are the symptoms of fibroidsLarger fibroids can cause you to experience a variety of symptoms, including:
- Heavy or painful bleeding during your menstrual cycle (menorrhagia).
- Bleeding in the middle of your menstrual periods.
- Bloating in your lower abdomen.
- Frequent urination (may occur when the fibroid puts pressure on your bladder).
- Pain during sex.
- Backache.
- Constipation.
- Chronic vaginal discharge.
- Inability to urinate or completely empty your bladder.
- It increases abdominal bloating (enlargement), making your tummy appear pregnant.
After you go through menopause, fibroid symptoms usually stabilize or go away as hormone levels in your body drop.
How does uterine fibroid pain feel?
If you have fibroids, there are a variety of sensations you may experience. If your fibroid is small, you may not feel anything and you may not even notice they are there. However, for larger fibroids, you may experience discomfort and even pain associated with the condition. Fibroids can cause back pain, severe menstrual cramps, sharp stabbing pains in your abdomen, and even pain during sex.
Can Fibroids Change Over Time?
Fibroids can actually shrink or grow over time. They can change size suddenly or permanently over a long period of time. This can happen for a variety of reasons, but on more than one occasion this change in fibroid size is in contact with the hormone measure in your body. When you have high levels of hormones in your body, fibroids can grow. This can happen at a reasonable time in your life, such as during pregnancy.
Your body releases high levels of hormones during pregnancy to support your baby’s growth. This hormone fluctuation also causes the fibroid to grow. If you know you had fibroids before pregnancy, talk to your healthcare professional. You may need to be monitored to see how the fibroid grows throughout pregnancy.
Fibroids can shrink as your hormone levels drop. This is common after menopause. When a woman goes through menopause, the amount of hormones in her body is much lower. This can cause the fibroids to shrink. Often your symptoms may improve after menopause.
Can I Conceive If I Have Fibroids?
Yes, you can get pregnant if you have uterine fibroids. If you already know you have fibroids when you are pregnant, your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a monitoring plan for fibroids. During pregnancy, your body releases high levels of hormones. These hormones support your baby’s growth. However, they can also cause your fibroids to grow.
 Fibroids Pregnancy
Fibroids PregnancyLarge fibroids can increase your risk of breech birth or fetal head misplacement, preventing your baby from transitioning to a correct fetal state. In very rare cases, your risk of preterm labor or cesarean delivery may be higher. In some cases, fibroids can contribute to infertility. It can be difficult to determine the exact cause of infertility, but some women can get pregnant after treatment for fibroids. Our previous topic: Is myoma a cause of infertility? have a look at the topic.
Can Fibroids Cause Anemia?
Anemia is a condition that occurs when your body does not have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen to your organs. It can make you feel tired and weak. Some women may develop a heavy craving for ice, starch or dirt. This is called pica and is associated with anemia. Women who have frequent or very heavy periods may have anemia.
Fibroids can cause your menstrual periods to be very heavy or even cause you to bleed mid-menstrual. Some treatments, such as oral iron pills, or if you are significantly anaemic, an iron infusion (via IV) can improve your anemia. If you are experiencing symptoms of anemia while you have fibroids, talk to your healthcare professional. (The symptom of this disease is the desire to “eat coffee grounds”!)
How Are Uterine Fibroids Diagnosed?
In most cases, fibroids are first discovered during a regular examination in women’s health institutions. They can be felt during a pelvic exam and can be found during a gynecological exam or during antenatal care. Your description of multiple times, heavy bleeding, and other related symptoms may alert your healthcare provider to consider fibroids as part of their diagnosis.
There are several tests that can be done to confirm fibroids and determine their size and location. These tests may include:
- Ultrasonography: This non-invasive imaging test creates a photo of your internal organs with sound waves. Depending on the size of the uterus, ultrasound can be done either transvaginally or transabdominally.
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This test creates detailed images of your internal organs using magnets and radio waves.
- Computed tomography (CT): A CT scan uses X-ray sights to create a detailed view of your internal organs from various angles.
- hysteroscopy : During hysteroscopy, your provider will use a device called a scope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera on the end) to look at fibroids inside the uterus. The scope is passed through your vagina and cervix and then moved into your uterus.
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG) : It is a detailed x-ray cinema where the contrast element is injected first and then x-rays of the uterus are taken. This is mostly used in women who have also undergone an infertility evaluation. Sharing area for those who have experienced the womb cinema (HSG)…
- sonohysterography : In this imaging test, a small catheter is inserted transvaginally and saline is injected into the uterine cavity through the catheter. This extra fluid helps create a clearer image of your uterus than you would see on a standard ultrasound.
- laparoscopy : During this test, your doctor will make a small incision (incision) in your lower abdomen. A thin flexible tube with a camera at the end will be inserted to take a close look at your internal organs.
How Is Myoma Treated?
Treatment for fibroids can vary depending on the size, number, and position of the fibroids and what symptoms they are causing. If you are not experiencing any symptoms from your fibroids, you may not need treatment. Small fibroids can often be left alone.
 myoma treatment
myoma treatmentSome women never experience any symptoms or any problems with fibroids. Your fibroids will be closely monitored over time, but you do not need to act quickly. Depending on the size or symptoms of your fibroid, periodic pelvic exams and ultrasound may be recommended by your healthcare professional.
If you are experiencing symptoms from your fibroids, you will often need treatment to help, including anemia from profuse bleeding, moderate to severe pain, infertility issues, or urinary and intestinal problems. Your treatment plan will depend on several factors, including:
- How many fibroids do you have?
- The size of your fibroids.
- Where your fibroids are located.
- The symptoms you experience with fibroids.
- Do you have any pregnancy wishes?
The most appropriate treatment option for you will also depend on your future fertility goals. If you want to have a baby in the future, some treatment options may not be an option for you. As you discuss treatment options, talk to your healthcare professional about your beliefs about fertility and your goals for the future.
Uterine fibroids are a common condition that many women experience throughout their lives.
In some cases, fibroids are small and cause no symptoms.
Other times, fibroids can cause strong symptoms.
If you experience any discomfort or pain, talk to your healthcare professional.
Fibroids are treatable and often your symptoms can be improved.
Drug Names Used in Myoma Treatment
- Over-the-counter (OTC) pain medications : These medications can be used to manage the discomfort and pain caused by fibroids. In the middle of OTC drugs are acetaminophen and ibuprofen.
- iron supplements: If you have anemia caused by heavy bleeding, your provider may also suggest that you take an iron supplement.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists : These drugs can be taken through a nasal spray or injection and work by shrinking your fibroids. They are sometimes used to shrink a fibroid before surgery, making it easier to remove the fibroid. However, these drugs are temporary and if you stop taking them, fibroids can grow back.
- Oral treatments : Elagolix is a new oral therapy indicated for the treatment of heavy uterine bleeding in premenopausal women with symptomatic uterine fibroids. Can be used up to 24 months. Talk to your doctor about the pros and cons of this treatment. Another oral therapy, Tranexamic acid, is an oral antifibrinolytic drug indicated for the treatment of cyclic heavy menstrual bleeding in women with uterine fibroids. Your doctor will monitor you during this therapy.
Important:It is valuable to talk to your healthcare professional about any medicine you take.
Birth control pill treatment for fibroids
The birth control pill can also be used to help with fibroid symptoms, especially heavy bleeding and menstrual cramps during and mid periods. Birth control can be used to help control heavy menstrual bleeding.
There are a variety of birth control options you can use, including oral contraceptive pills, intravaginal contraception, injections, and intrauterine devices (IUDs).
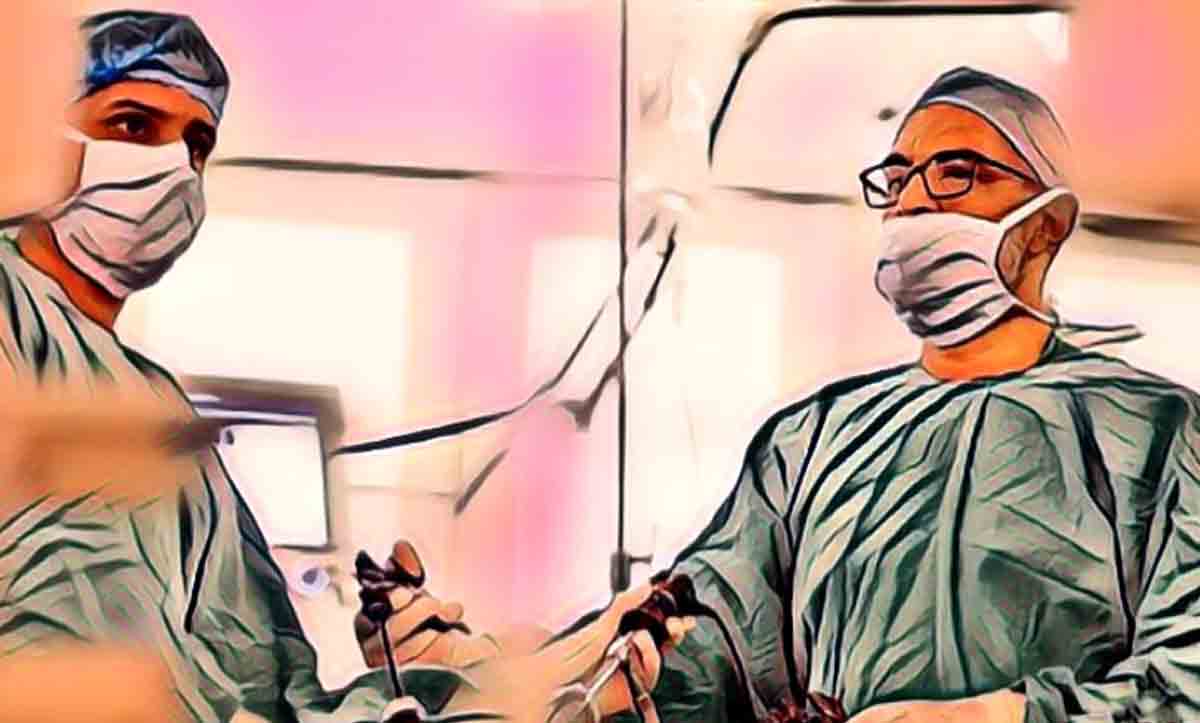
How is Myoma Surgery Performed?
There are several factors to consider when talking about the different types of surgery to remove the fibroid. The size, position, and number of fibroids not only affect the type of surgery, but your wishes for future pregnancies can also be a valuable factor when developing a treatment plan.
 How is myoma surgery done?
How is myoma surgery done?While some surgical options preserve the uterus and allow you to conceive in the future, other options may damage or remove the uterus. Myomectomy is a procedure that allows removing fibroids without damaging the uterus.
How big do fibroids need to be before they can be surgically removed?
The normal uterus size is the size of a lemon or 8 cm. There is no definitive fibroid size that would require automatic removal. Your healthcare provider will identify the symptoms that are causing the problem. For example, fibroids the size of a marble, if they are located in the uterine cavity, may be associated with deep bleeding. Fibroids the size of a grapefruit or larger can cause you to experience pelvic pressure, as well as make you look pregnant and see increased abdominal enlargement, which can cause an enlarged abdomen.
It is valuable to discuss symptoms from your healthcare provider and the patient that may require surgical intervention.
What Are the Types of Myomectomy?
There are several types of myomectomy. The type of procedure that may work best for you will depend on where your fibroids are, how large they are, and the number of fibroids.
 myomectomy
myomectomyVariants of myomectomy to remove fibroids may include:
Hysteroscopy Myoma Surgery
This procedure is done by inserting a scope (a thin, flexible, tube-like instrument) into the uterus through the vagina and cervix. No incision is made during this process. During the procedure, the surgeon will use the scope to cut through the fibroids. The physician will then remove the fibroids.
What is Laparoscopic Myomectomy?
In this procedure, the surgeon will use a scope to remove the fibroids. Unlike hysteroscopy, this procedure involves making several small incisions in your abdomen. This is how the scope will enter your body and exist. This procedure can also be performed with the help of a robot.
Laparotomy Myomectomy Surgery
This method is open myoma surgery. During this process, an incision is made in your abdomen and the fibroids are removed with this large incision.
If you are not planning a future pregnancy There are additional surgical options your healthcare provider may recommend. If pregnancy is desired and there are surgical approaches to remove the uterus, these options are not recommended. These surgeries can be very effective, but they typically prevent future pregnancies. Surgery to remove fibroids may include:
Hysterectomy Surgery
During this surgery, your uterus is removed. The only way to beautify fibroids is hysterectomy. When you completely remove your uterus, the fibroids can’t come back and your symptoms go away. If your uterus is removed alone, if the ovaries remain in place, you won’t go into menopause after a hysterectomy.
This procedure may be recommended if you are experiencing heavy bleeding from your fibroids or have large fibroids. When recommended, the most minimally invasive procedure is recommended to perform hysteroscopy. Minimally invasive procedures include vaginal, laparoscopy, or robotic approaches.
Uterine fibroid embolization
This procedure is performed by an interventional radiologist working with your gynecologist. A small catheter is inserted into the uterine or radial artery and the small particles are used to block blood flow from the uterine artery to the fibroids. Loss of blood flow shrinks fibroids and improves fibroid symptoms.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
It is a safe and effective treatment for women with symptomatic uterine fibroids and can be given by laparoscopic, transvaginal or transcervical approaches.
There is also a newer procedure called magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) guided focused ultrasound that can be used to treat fibroids. This technique is actually done while you are inside an MRI machine. You are placed inside the machine that allows your provider to see the fibroids clearly, and then an ultrasound is used to send targeted sound waves to the fibroids.
This damages the fibroids.
Are there any risks associated with fibroid treatment?
Any treatment can have risks. Medications can have side effects and some may not be suitable for you. Before starting a new medication, talk to your healthcare provider about all medications you can take for other medical conditions and your full medical history. If you experience side effects after starting a new medication, call your doctor to discuss your options.
There are always risks in the surgical treatment of fibroids. A random surgery puts you at risk of infection, bleeding, and a random inherent risk associated with surgery and anesthesia. An additional risk of fibroid removal surgery may include future pregnancies. Some surgical options can prevent future pregnancies.
Myomectomy is a procedure that only removes fibroids and allows for future pregnancies. However, women who have had a myomectomy may need to deliver their future baby via cesarean section (cesarean section).
Can fibroids be prevented?
Generally, you cannot prevent fibroids. You can reduce your risk by maintaining a healthy body weight and having regular pelvic exams. If you have small fibroids, develop a plan with your healthcare provider to monitor them.
Do fibroids naturally disappear?
In some women, fibroids may shrink after menopause. This happens due to a decrease in hormones. Your symptoms may go away when the fibroids shrink. Small fibroids may not need treatment if they do not cause any random symptoms.
- On-Site Comments















Comment